In today’s digital age, graphics are essential for online audiences. Whether you’re a graphic designer or photographer or simply an individual looking to enhance your image editing skills, mastering color correction in Photoshop is an essential skill that can raise your work to new heights. In this complete guide, we will deeply investigate the art of color correction, discovering the details of this essential image editing feature.

Understanding the Basics of Color Correction
Color correction in Photoshop is the process of altering and enhancing the colors of an image to achieve a desired look or to correct any imperfections. It’s a vital step in the post-production workflow, ensuring that your pictures appear visually appealing and accurate to life. Here’s a breakdown of the critical concepts you need to grasp:
1. Color Modes as RGB vs. CMYK
Empathetic color modes are the basis of effective color correction. Photoshop proposes two primary color modes – RGB (Red, Green, Blue) and CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black). RGB is cast-off for digital shows, while CMYK is mainly for print. Selecting the correct color mode is vital to upholding color correctness.
2. Histogram Analysis
Histograms are graphical pictures of an image’s tonal range. Knowledge of reading and understanding histograms permits you to classify and precisely expose issues, safeguarding that your imageries have a balanced delivery of light and dark areas.
Mastering Color Correction Techniques
Now that we’ve enclosed the basics let’s dive into the applied methods that will help you become a color correction maestro:
3. Levels Adjustment
The Levels alteration tool in Photoshop is an influential ally in color correction. It permits you to precisely regulate the brightness, contrast, and tonal range of a copy. You can highlight hidden particulars by slowing the sliders and popping your images.
4. Curves Adjustment
Curves are like the progressive form of Levels. They deliver even more control over your imagery’s tonal range and color balance. S-curves can add depth and wealth to your photos.
5. Color Balance
Color Balance permits you to modify the colors in your image. You can correct unwelcome color casts or make specific moods by regulating the balance between the primary colors – red, green, and blue.
6. Selective Color
Selective Color is a tool that allows you to tweak individual color channels. This can be particularly useful for isolating and modifying specific colors within an image.
7. Hue/Saturation
Hue/Saturation allows you to alter the color of objects within an image or increase their fullness for a more vibrant look. It’s faultless for making specific basics stand out.
8. Photo Filters
Photo Filters fake the consequence of using colored sieves in photography. They can add temperateness or cold to your images, ornamental to the overall mood.
Advanced Color Correction Techniques
For those seeking to take their color correction services to the next level, here are some advanced techniques:
9. Gradient Maps
Gradient Maps are an inspired way to map colors to the tonal range of an image. They agree on artistic and dramatic color effects.
10. LUTs (Look-Up Tables)
LUTs are pre-made Color presets that can punctually alter the look of your photos. They are mainly used in the film and photography industry for color grading.
Color Correction Using Photoshop
Color Correction Might Enhance That Extra Punch to Your Digital Images!
This is one thing I have seen as I talk to people, look at photos and 5call forums. Despite all the bells and tots modern excision programs have, a central point is being ignored at the editing stage. That is color correcting any unwelcome color corrections in digital images. We can do this with any version of Adobe Photoshop.
Nowadays, it’s not to “grow” our images every step of the way. Your rejections from film photography would have been wholly edited at professional labs. They would have modified the color, among other things, for you.
It is, therefore, more pronounced when an image has a color cast to it, usually red or yellow. Which can make people think there is a problem with their camera. An imprecise color cast is quite regular. It typically seems when you have been gunfire in low light, perhaps indoors, with no studio lights or flash, or maybe you or the camera had set the improper white balance.
For example;
This was taken rapidly under typical inside lighting conditions. These are the same as the lights used at people’s houses or weddings!
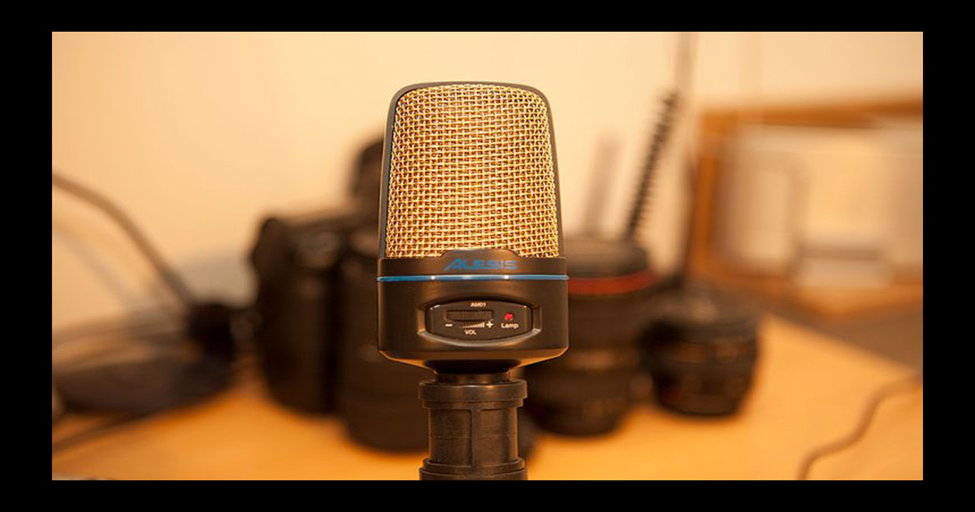

Many twosomes don’t like flash being used at their wedding. It is unavoidable, therefore, that you will end up with some color molding. There is a simple way around this, which I will cover below. Once you grasp it, you will want to try this out through many of your images. It can influence your pictures.
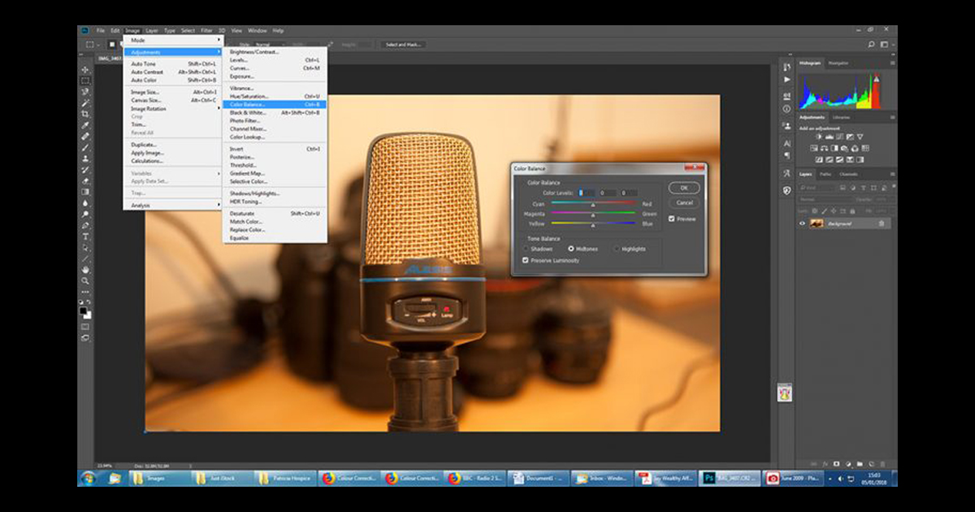
As this image has a relatively large quantity of red and yellow cast, we need to change those colors. So, with the “Mid-tones” box marked in the tone equilibrium area of the box, slide the Cyan-Red slider to the left. Don’t slide too much; reduce the red hue, but don’t. After that, slide the yellow-blue slider to the right to reduce the yellow hue. Again, not too much.
If you tick the showing box, you will see the changes happen as you make them. Each image is dissimilar and will need variable amounts of alteration. For my image, in the mid-tones section, I abridged the Cyan – Red slider to -20 and amplified the Yellow – Blue to +20.
Highlights and Tone Balance
If you don’t see a considerable change, don’t worry! There is more. Now, tick the Tourist attractions box in the Tone Balance area, make similar changes, and cut the red and yellow hues. For my image, I reduced the red to -20 and the yellow to +20, and the consequence is this;
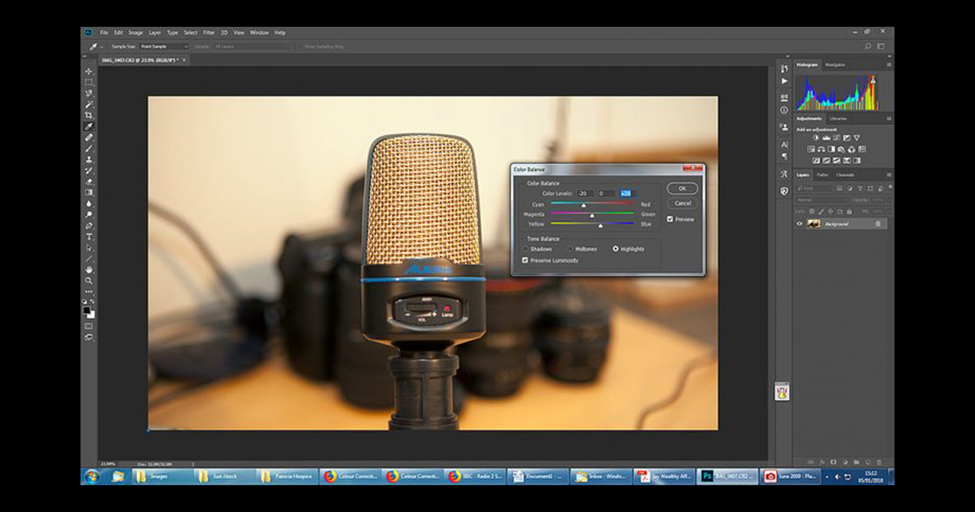
In later forms of Photoshop, you can just hit “auto color,” as the color corrections are now attractive and precise. However, this method permits you more options and originality. Lastly, tick the glooms box and make minor changes there. It’s too much, and your difference will hurt, so make gradual changes and see what happens.
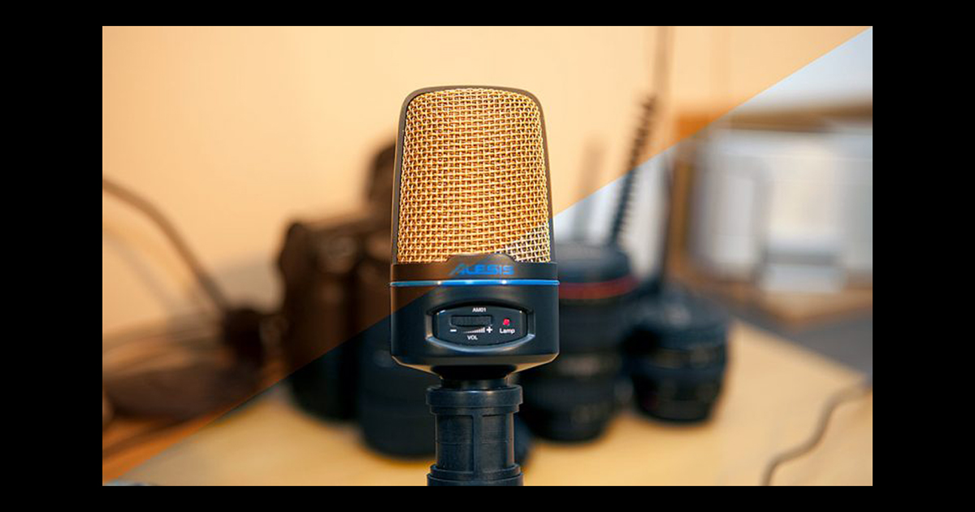
The difference is quite apparent, as you can see above. The colors are appropriately balanced, and the grey/black items have returned to their natural color.
You can use high ISO (3200 or 6400+) indoor shooting with modern Digital SLRs like the Canon EOS 5D Mark IV. This removes the essential flash if you use this method with the help of noise decrease software such as Neat Image.
Color Correction Using Photoshop Of course, color correction using Photoshop is valuable in many features other than wedding photography.

I do a lot of inner work, and occasionally, it is not applied or essential to set up the studio lights for portraits such as a quick kitchen shot.
Support setup using natural light will do, knowing I can accurately see the color balance later.
Photo filter
To regulate the quantity of color practical to the Image, use the Thickness slider or physically enter a fraction in the Density box. A higher thickness results in a sturdier color adjustment.

(Optional) Select Preserve Luminosity to stop altering the luminosity values in the portraits while changing the color. By default, this option is permitted to uphold the overall tonal balance in your Image.
Enable Showing to view your edits on your Image. Click OK to smear changes and stop exiting the Photo Filter dialog.
Change color balance using Photo Filter.
You can access the Photo Filter choice from any of the following locations:
In the Changes panel, click the Photo Filter icon () icon. Soon after that, Choose Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Photo Filter. From the New Layer dialog box, Click OK.
You can also pick Image> Adjustments > Photo Filter. However, this method smears critical adjustments to the image layer and castoffs image info, so you cannot reinstate the original Image.
Once you choose the Photo Filter option, do the following:
In the Possessions panel that opens, you can also select a custom color filter:
Filter: For a preset filter, select the Filter choice and pick one of the presets from the drop-down list.
Color: For a custom filter, choose the Color picker. Click the color box, and try Adobe Color Picker to stipulate a color for a custom color filter.
Conclusion
Mastering color correction in Photoshop is a trip that needs exercise and a keen eye for detail. With the techniques drawn in this guide, you’ll be well-appointed to improve your images, correct inadequacies, and uncheck your originality. Whether you’re an expert photographer, a graphic designer, or a fanatic, the power to operate colors in Photoshop is at your fingertips.
So, roll up your covers, open Photoshop, and start testing with these color correction techniques. Your images will look outstanding.
Summarizing the video through a Q&A session
What are the critical stages involved in blending images in Photoshop?
The critical steps in combination images in Photoshop include correcting lightness, color, and saturation, sketching ambient light from the sky and rim light from the sun, adding aperture belongings for bokeh, smearing final light effects, and executing color grading using the Camera Raw filter.
How can one eliminate backgrounds from pictures in Photoshop professionally?
Background removal in Photoshop can be proficiently done using the Color Range tool, wherever one can choose precise colors, such as the sky, create a mask, and refine the selection. Moreover, masking techniques and tools like the Clone Stamp can assist in eliminating multifaceted backgrounds with precision.
What considerations are significant for corresponding the colors and illumination of dissimilar elements in a compound image?
When corresponding colors and lighting in a merged image, it’s vital to blend the elements’ nimbleness values, saturation, and colors. Paying attention to the way and strength of light sources, such as sunlight and ambient light from the sky, helps make a unified and truthful composition. Using change layers like Discerning Color and Color Balance, along with methods like blending modes and blend-if sliders, can aid in attaining a unified addition of elements.
How can one improve the overall graphic appeal of a compound image finished post-processing techniques?
The attractive visual appeal of a compound image can be attained through post-processing techniques such as smearing color grading using tools like Bends and Camera Raw filter, adding atmospheric effects like haze or fog, and refining highlights and shadows to generate complexity and dimension. Additionally, joining glow effects, regulating contrast, and fine-tuning white balance pay to making a polished and charming final image.

